Published On Aug 31, 2023
📝 All videos on Cardiovascular System: https://www.nonstopneuron.com/post/ph...
🌐 Explore our entire animation video library: https://www.nonstopneuron.com/
● Follow me at:
• Instagram: / nonstopneuron
• Facebook: / nonstopneuron
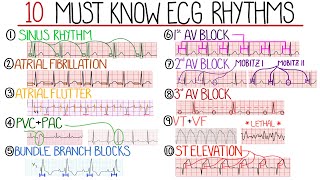
Everything Normal Electrocardiogram: From Getting 12 Lead ECG to How Normal Waves are Produced | Normal EKG | Normal ECG
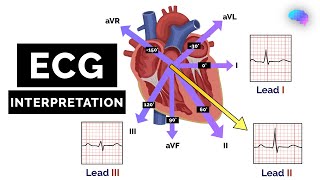
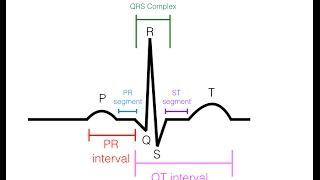
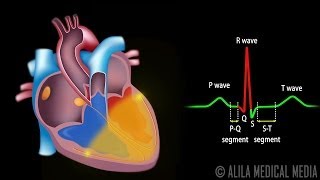
An electrical meter or a lead, records the potential at its positive end as compared to the negative end. If it's at a positive potential, it shows a positive reading. And if it's at a negative potential, it shows a negative reading. If the potential on both ends is the same, it shows no reading. It can record only that portion of the electrical activity that falls parallel to the direction of the electrode placement. The perpendicular activities, are not recorded. In the heart, the activities happen in many directions in three dimensions. So for better mapping of these activities, we use multiple leads. Three standard-bipolar limb·leads are created on the coronal plane, by connecting electrodes at both arms and the left leg. These three connections represent the tips of Einthoven's triangle around the heart. 3 augmented-unipolar limb·leads are created using the same electrodes. Each augmented lead, uses one of these electrodes as the positive end, and a combination of the remaining two as a negative end. For 6 chest·leads or precordial·leads on the transverse plane, a positive electrode is placed on the chest, at different points around the heart. And they all use a common negative connection obtained by combining all three electrodes on the limbs. This is equivalent to putting their negative electrodes in the middle of the heart. Each of these 12 leads records the heart's activity from a unique angle. So some areas are better recorded in some leads than others. In normal ECG, the P wave is produced by atrial depolarization, the QRS complex is produced by ventricular depolarization. Atrial repolarization occurs along with the QRS complex, so it's obscured. Ventricular repolarization produces the T wave. Different intervals studied in ECG are the P-Q interval or PR interval, QT interval, ST segment, and RR interval.
Chapters:
00:00 Intro
00:38 Basics of Recording Electrical Activity
07:57 12 Lead ECG: Introduction
09:11 Standard Bipolar Limb Leads
11:45 Augmented Unipolar Limb Leads
13:26 Unipolar vs Bipolar Lead: The Difference
13:51 All Leads on Frontal Plance: A Summary
14:25 Precordial Leads (Chest Leads)
15:51 12 Leads: Summary and Importance
17:46 How Normal ECG Waves are Produced
25:27 Intervals and Segments in ECG
26:54 Summary
Dr Vipul Navadiya
Nonstop Neuron
Medical Animation
Medical Animation Videos
Physiology
DISCLAIMER: This video is for education purposes only. Although every effort is made to ensure the accuracy of the material, viewers should refer to the appropriate regulatory body/authorized websites, guidelines, and other suitable sources of information as deemed relevant and applicable. In view of the possibility of human error or changes in medical science, any person or organization involved in the preparation of this work accepts no responsibility for any errors or omissions, or results obtained from the use of information in this video.