Published On Apr 27, 2021
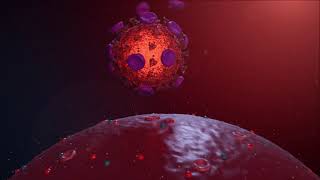
Since the outbreak of COVID-19, there has been a great leap in mRNA vaccine development.
When mRNA (messenger RNA) vaccines are injected into a patient, tiny lipid vesicles transport mRNA molecules through the body fluids and merge with immune cells, called antigen-presenting cells (APCs). mRNA vaccines work to instruct APCs to manufacture proteins called antigens that evoke an immune response to the threat.
How do mRNA vaccines compare to conventional vaccines?
Conventional vaccines directly introduce antigenic proteins that stimulate an immune response in the host. mRNA vaccines introduce mRNA encoding a disease-specific antigen to trigger the body’s normal infection-fighting process How mRNA vaccines target COVID-19 Coronavirus mRNA vaccines spur the production of these foreign antigens within the body prepares the immune system to recognize and memorize this viral antigen so it is ready to fight off future infections caused by virus with the same antigen.
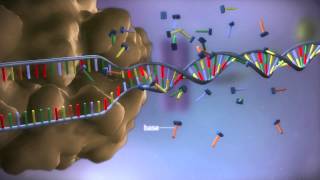
How mRNA vaccines work within human cells
mRNA is like a blueprint that carries the information cells use to produce different proteins. Inside human cells two steps: - Within the nucleus of the cell, the information encoded in DNA is transferred to mRNA via a process called transcription. - The mRNA moves from the nucleus to the cytoplasm where ribosomes translate the mRNA into protein, which performs functions of our cells and tissues.
For more information on mRNA vaccines to fight the spread of COVID-19, visit https://www.cas.org/blog/covid-mrna-v...
For more information about how CAS data scientists are approaching COVID-19 and for resources to fuel your research, visit https://www.cas.org/resources/covid19